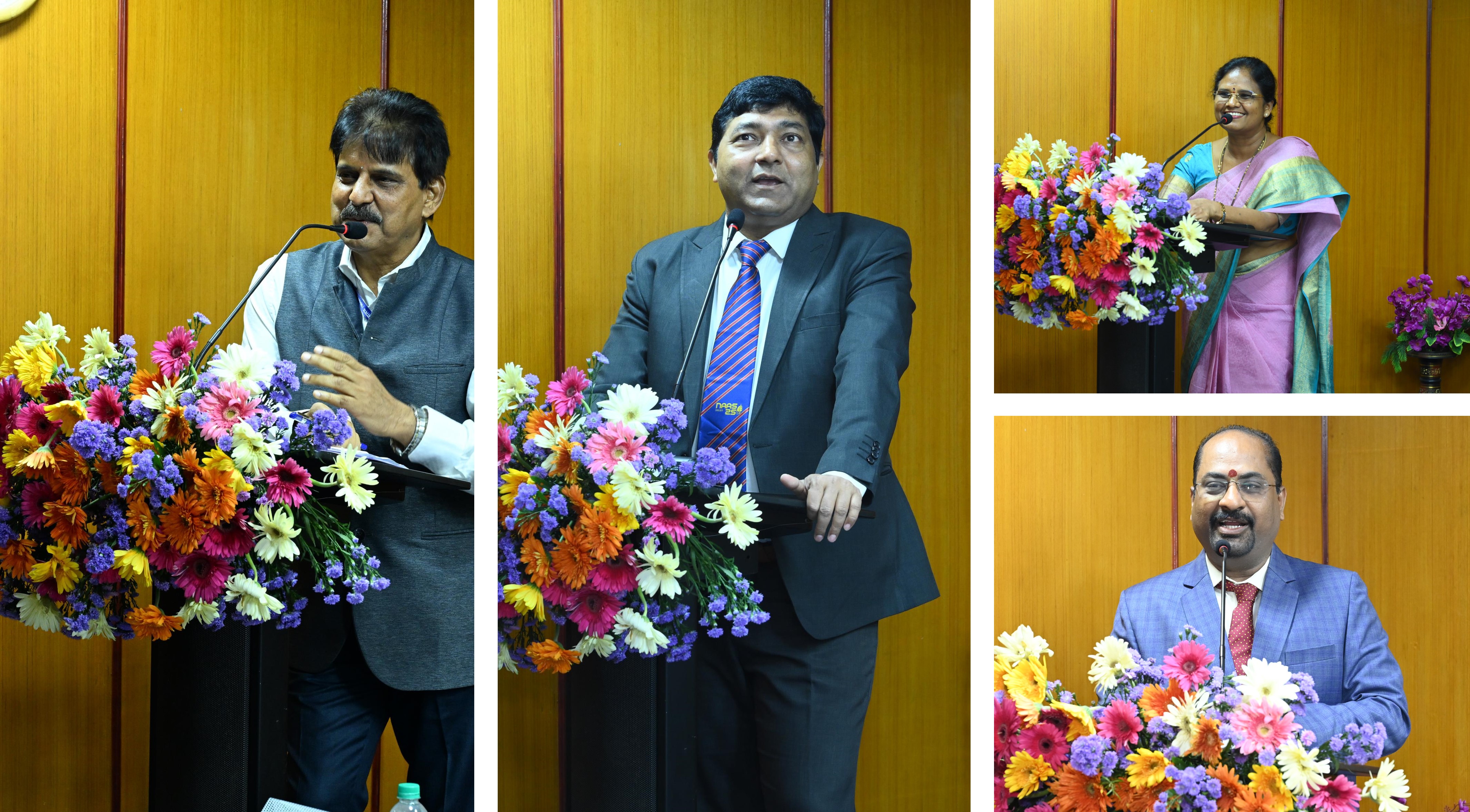
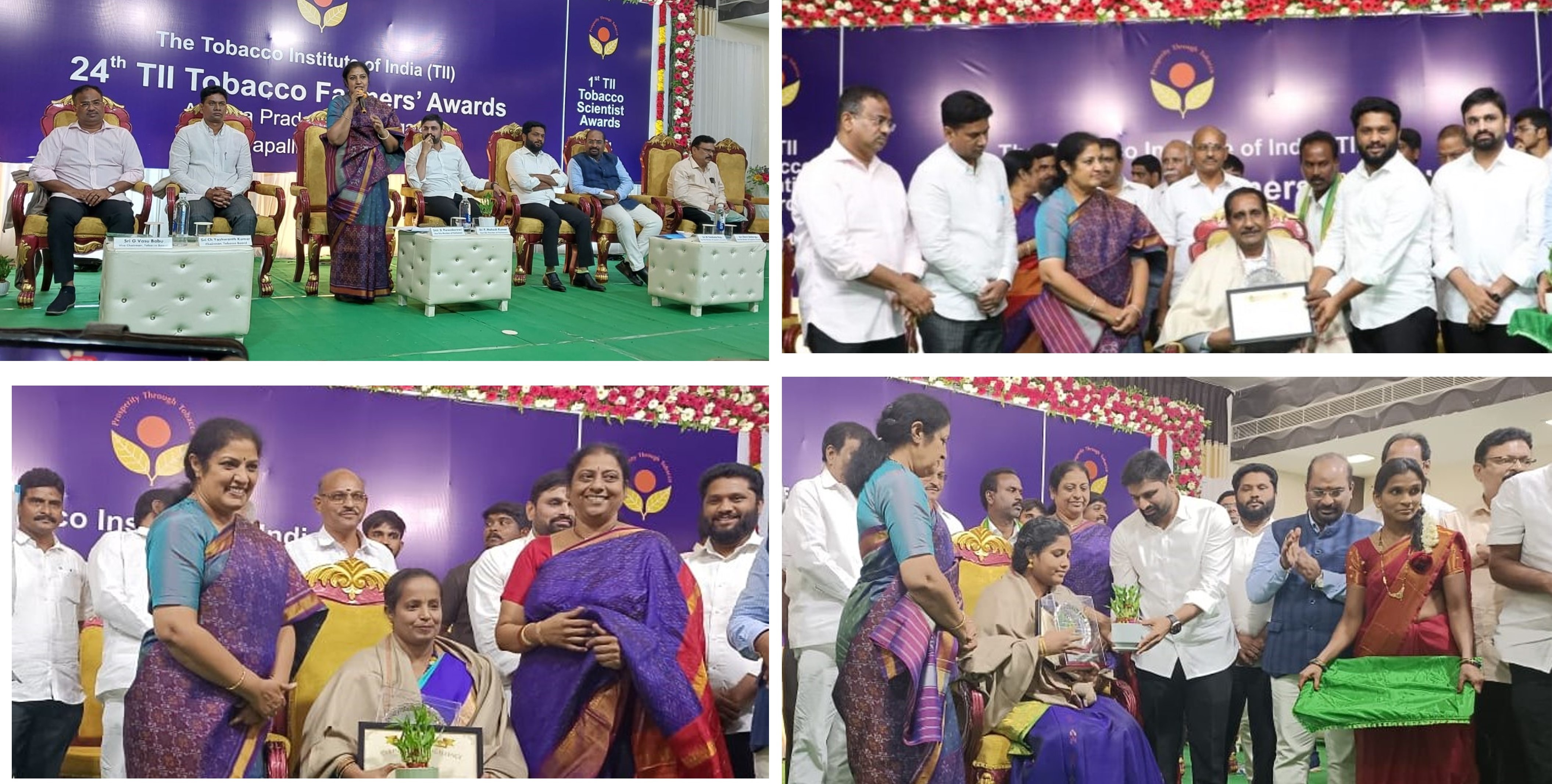
In India, organized tobacco research has its origin in the mid-1930s with the establishment of the Cigarette Tobacco Research Station at Guntur under the patronage of the formerly Imperial Agricultural Research Institute (IARI), New Delhi. With the growing importance of tobacco in the national economy, the Government of India constituted the Indian Central Tobacco Committee (ICTC) to establish the Central Tobacco Research Institute (CTRI) in 1947. Subsequently, the institute was brought under the aegis of the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) in the year 1965. Since its origin, the Institute has been commanding national tobacco research and has made an outstanding contribution to the growth and development of tobacco science in India. Through its long voyage of 75 years, the Institute has evolved into a tobacco research network system with 6 research stations located in different states across the country, one All India Network Project on Tobacco, and 2 Krishi Vigyan Kendras catering to the research needs of varied tobacco types grown across the country. Tobacco is one of the important high-value commercial crops in India. It is grown in an area of 0.433 million hectares over 15 states in India. Presently, India stands second in production of tobacco (758 million kg) in the world after China. It provides employment directly and indirectly to 45.7 million people and contributes to nearly Rs.22, 737 crore as excise duty and Rs. 9740 crore in terms of foreign exchange to the national exchequer. A unique feature of tobacco production in India is that myriad styles of Flue-cured Virginia (FCV) and non-FCV tobacco are cultivated under widely differing agro-ecological situations. The FCV, bidi, hookah, chewing, cigar wrapper, cheroot, burley, Oriental, HDBRG, Lanka, Pikka, Natu, etc. are the main types of tobacco grown in the country, with FCV and Burley tobacco being the main exportable types.



 GOVERNMENT OF INDIA
GOVERNMENT OF INDIA  ||
MINISTRY OF AGRICULTURE AND FARMER'S WELFARE
||
MINISTRY OF AGRICULTURE AND FARMER'S WELFARE
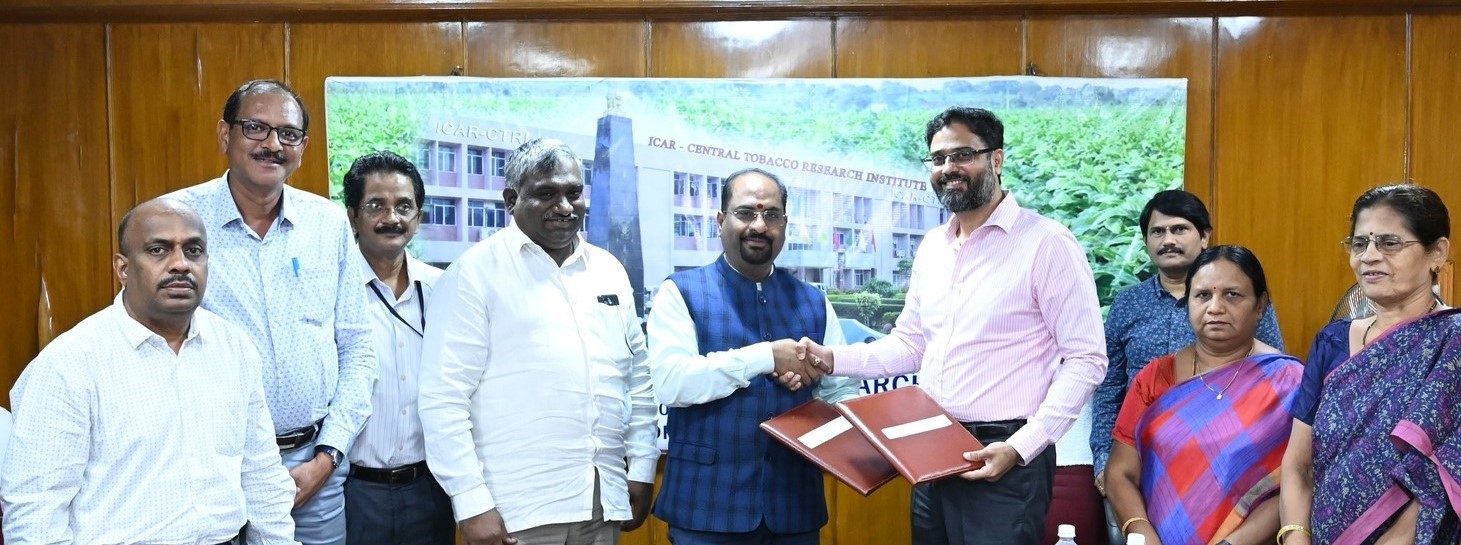
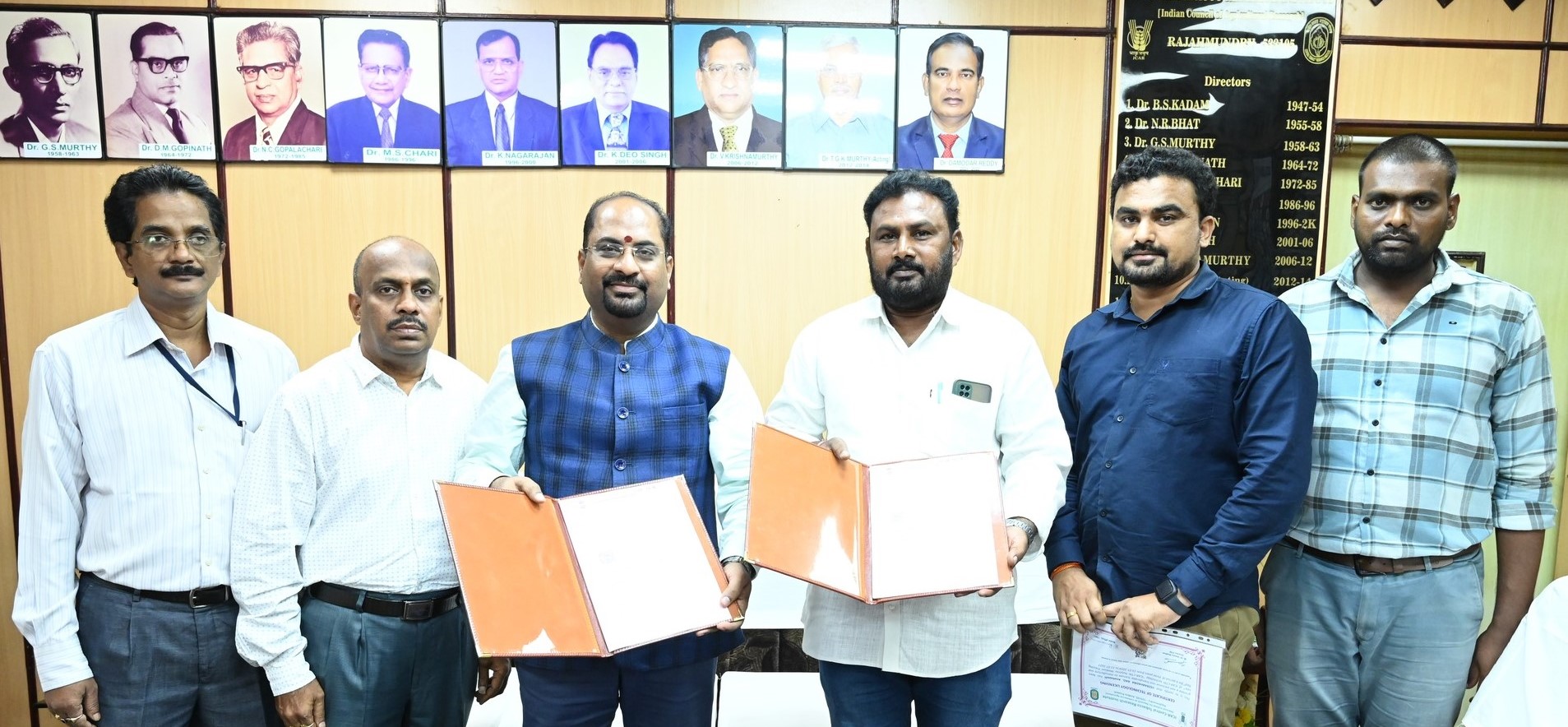











 Notification for Engagement of YP-I positions in Accounts & Administration Depts. on Contractual Basis at ICAR-CTRI, Rajahmundry dated 25.07.2024
Notification for Engagement of YP-I positions in Accounts & Administration Depts. on Contractual Basis at ICAR-CTRI, Rajahmundry dated 25.07.2024